Whole blood B cell activation
B cell responses are a vital part of the adaptive immune response, resulting in antibody production to neutralize infections. Excessive B cell activation can, however, also lead to adverse health effects, such as autoimmunity. Therefore, determining the influence of your compound on B cell activation may be of interest to you, whether you are looking for on-target or off-target effects.
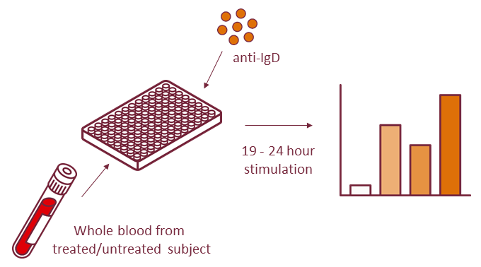
The B cell activation assay is a whole blood assay used to investigate B cells responsiveness after B cell receptor (BCR) triggering (see scheme). In this case, the BCR triggering is mimicked by incubation with anti-IgD. Anti-IgD crosslinks the BCRs on the B cell membrane and activates the cell. Activation of the BCR induces upregulation of the activation marker CD69, which can be analyzed by flow cytometry in combination with CD19 and CD27 to identify naïve B cells.
Advantages of the whole blood B cell activation assay
- 350 µl of whole blood per subject is sufficient for read-out
- Assay has been set up according to ISO15189 regulations and can therefore directly be used in clinical trials
- No pre-selection of cells necessary
- High-throughput measurement of many samples possible
Example of whole blood B cell activation
Assesing B cell activation after in vivo compound dosing
 Heparinized blood was collected at several time points after subjects received an anti-inflammatory drug or a placebo. After blood collection, B cells in whole blood were stimulated with anti-IgD (n=2), or left unstimulated (n=2). The samples were stained the following day with anti-CD19, anti-CD27 and B cell activation marker anti-CD69. Subsequently, the erythrocytes were lysed to clean up the sample for flow cytometry. The white blood cells were fixed and analyzed by flow cytometry. Mean % B cell activation is expressed as the percentage of CD69+CD19+CD27- naïve B cells.
Heparinized blood was collected at several time points after subjects received an anti-inflammatory drug or a placebo. After blood collection, B cells in whole blood were stimulated with anti-IgD (n=2), or left unstimulated (n=2). The samples were stained the following day with anti-CD19, anti-CD27 and B cell activation marker anti-CD69. Subsequently, the erythrocytes were lysed to clean up the sample for flow cytometry. The white blood cells were fixed and analyzed by flow cytometry. Mean % B cell activation is expressed as the percentage of CD69+CD19+CD27- naïve B cells.
Our other B cell assays
We also offer other methods of B cell activation/effector function analysis.
Our other whole blood assays
By using whole blood, interactions between different cell types and serum components can still occur, reflecting the in vivo situation.

